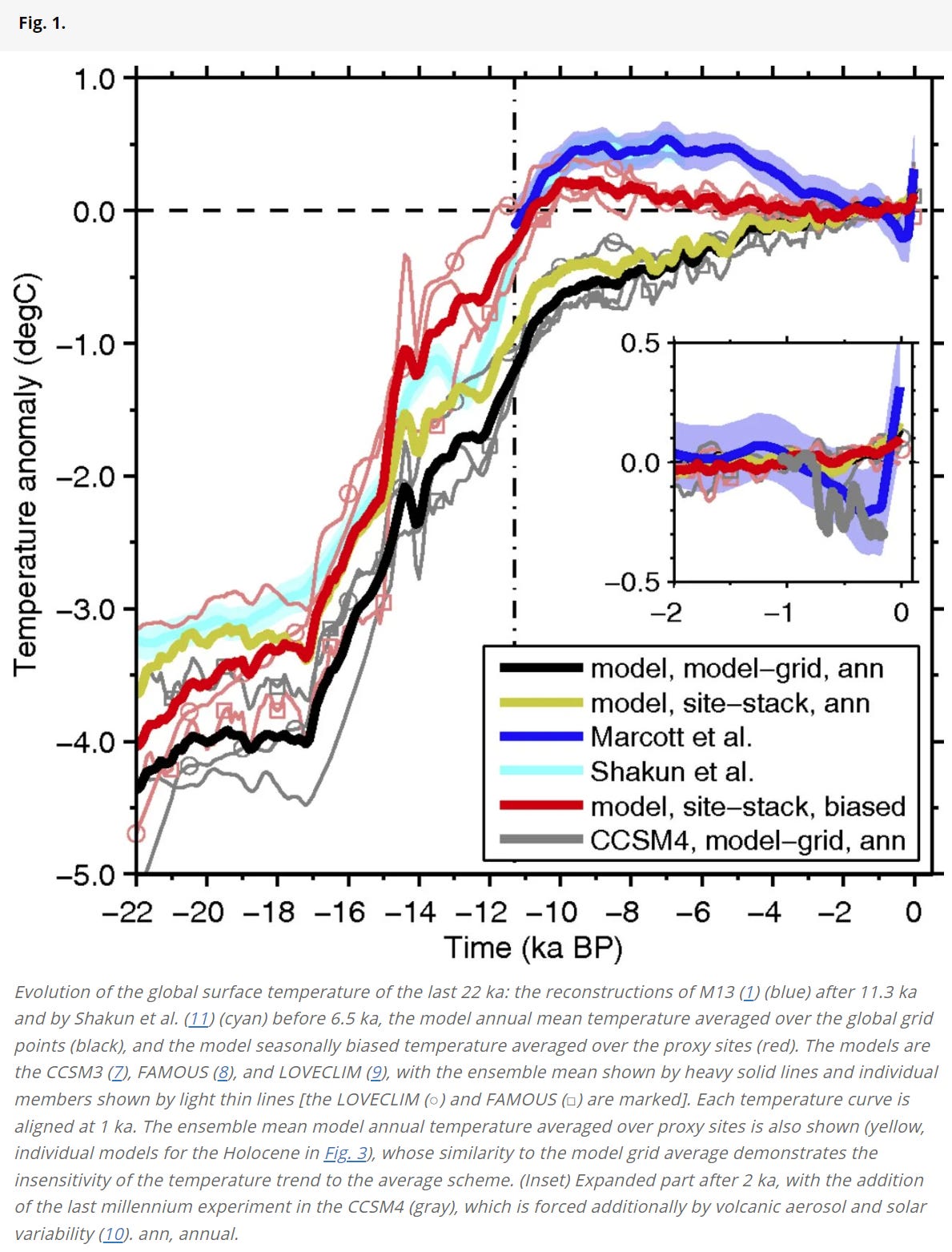
Temperature fluctuations throughout the Holocene (the last ~12ky)…
The Holocene epoch, the current geological epoch that began about 12,000 years ago after the last major ice age, has witnessed numerous climate fluctuations. The overall pattern of the Holocene can be characterized by a general warming trend with intermittent periods of cooling.
Early in the Holocene, the Earth experienced a rapid warming phase known as the Holocene Thermal Maximum, which occurred around 9,000 to 5,000 years ago, depending on the location. This period marked the warmest point in the Holocene, with global temperatures around 0.5-2°C warmer than the mid-20th century baseline. During this period, it was likely that summers in the Northern Hemisphere were significantly warmer, leading to the retreat of the last remaining glaciers in North America and Europe.
However, following the Holocene Thermal Maximum, there was a gradual cooling trend that occurred over several millennia, now known as the Neoglacial period. This period began around 5,000 years ago and continued until the start of the Industrial Revolution. Interestingly this cooling trend occurred simultaneously with a gradual increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations, known as the Holocene temperature conundrum, and highlights the relative insensitivity of temperature and GHG concentrations.
Within the Neoglacial period, the Earth experienced several pronounced cold periods. These include the Little Ice Age, which occurred from about 1300 to 1850 AD and was characterized by significantly cooler temperatures, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. Also of note is the Medieval Warm Period, occurring roughly between 950 to 1250 AD, which interrupted the general cooling trend.
The end of the Little Ice Age marked the beginning of the current period of warming. Today's temperatures are approaching those of the Holocene Thermal Maximum in some areas while others remain significantly cooler. The Holocene's climate history underscores the short-term natural variability of the climate system.
Temperature fluctuations throughout the Pleistocene (~2.5mya to 12kya)…
The Pleistocene epoch, ranging from about ~2.5 million years ago to about 11,700 years ago, was marked by repeated glacial-interglacial cycles, where the Earth oscillated between colder glacials, often called "ice ages," and warmer interglacials. These fluctuations were driven by variations in the Earth's orbit and axis tilt, known as Milankovitch cycles, which affect the amount of solar radiation reaching different parts of the Earth's surface.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Irrational Fear to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.